|
Head: Agnieszka Dobrzyń Anna Dziewulska, |
 |
Research profile
Our research group carries out multidisciplinary studies on signaling and transcriptional cascades that have far-reaching implications on cell metabolism and human metabolic diseases, mainly type 2 diabetes. Our main priority is to understand the role of lipid metabolites and epigenetic modifications of gene expression in the development of insulin resistance and pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. We are also interested in gaining insights into the functional role of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) in regulation of pancreatic islet metabolism and development because it will increase our awareness of lipid partitioning, and may have important implications for pathogenesis of the Metabolic Syndrome. Our research is focused on signaling pathways affected by fatty acids during pancreatic organogenesis in healthy and insulin resistant models and determination the role for lipid mediators in pancreatic beta-cell – alpha-cell communication as well as the cross-talk between insulin resistant tissues (i.e. skeletal muscle and adipose tissue) and pancreatic islets. Our genuine intension is to provide solid foundation for knowledge about the role of lipid mediators in pancreatic islet organogenesis and function, and to increase understanding of molecular mechanisms that trigger pancreatic beta-cell adaptation towards systemic insulin resistance. We are also a partner of a multi-sectorial consortium which ultimate goal is to generate Human Bionic Pancreas – a 3D functional scaffold for islet transplants that could become a full-fledged method for the treatment of diabetes.
Current research activities:
- metabolic regulation of the DNA damage response in pancreatic beta- cells in different models of type 2 diabetes,
- lipid signaling in regulation of organogenesis and embryonic development of pancreatic islets,
- epigenetic regulation of pancreatic islets’ metabolism and function,
- metabolic and genetic abnormalities in endocannabinoid-related regulation of insulin sensitivity,
- heat shock protein HSP72 in the development of lipid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle,
- adipose-derived stem cells as a source of insulin- and glucagon- producing cells for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications.
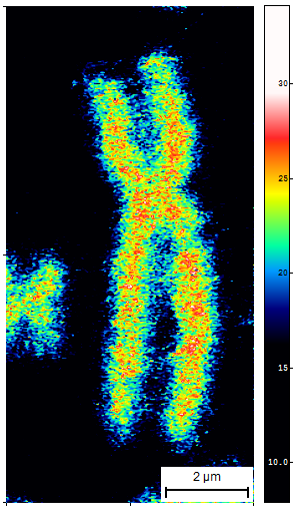
Fig. 1. Methyl-group spatial distribution within chromosome 1 of pancreatic beta-cell. |
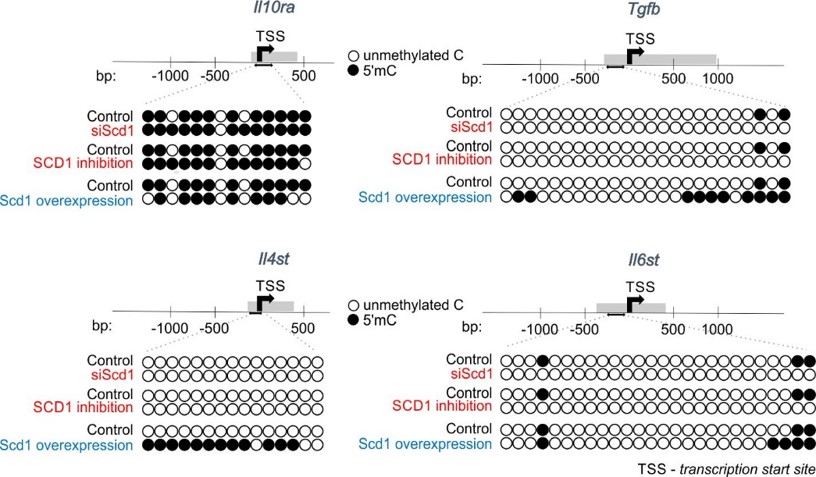
Fig. 2. SCD1 regulates promoter methylation of genes involved in inflammatory response. Representative bisulfite sequencing analysis of CpG sites within promoters of Tgfb, Il10ra, Il4st, Il6st genes. |
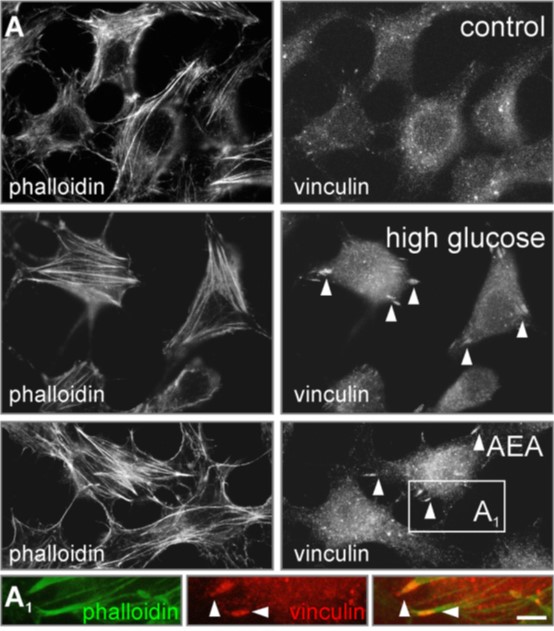
Fig. 3. Activation of CB1 receptor induces insulin secretion via cytoskeletal remodeling. |
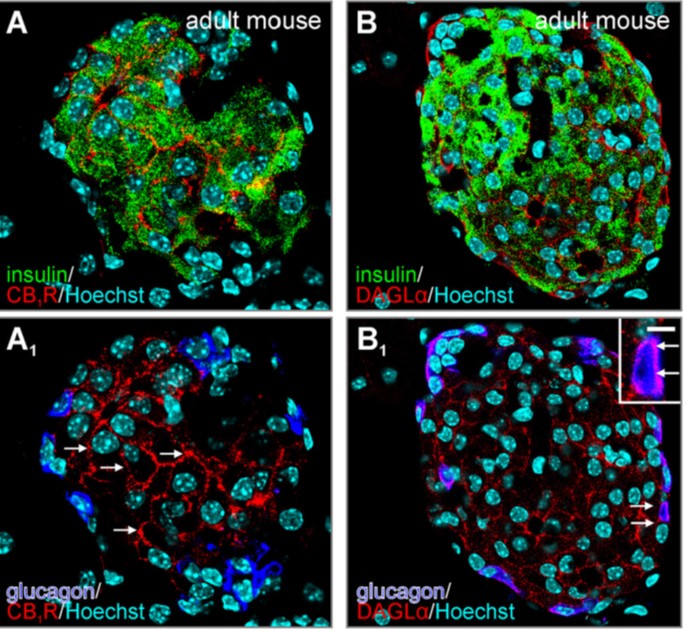
Fig. 4. Organization of endocannabinoid signaling networks in pancreatic islets. |
|
|
Fig. 5. SCD1 regulates gene transcription in skeletal muscle. Microarray analysis of muscle transcriptome of wild type mice (Control), Scd1 knock-outs (Scd1 KO), and mice with muscle-specific over-expression of Scd1 (Scd1 Tg). |